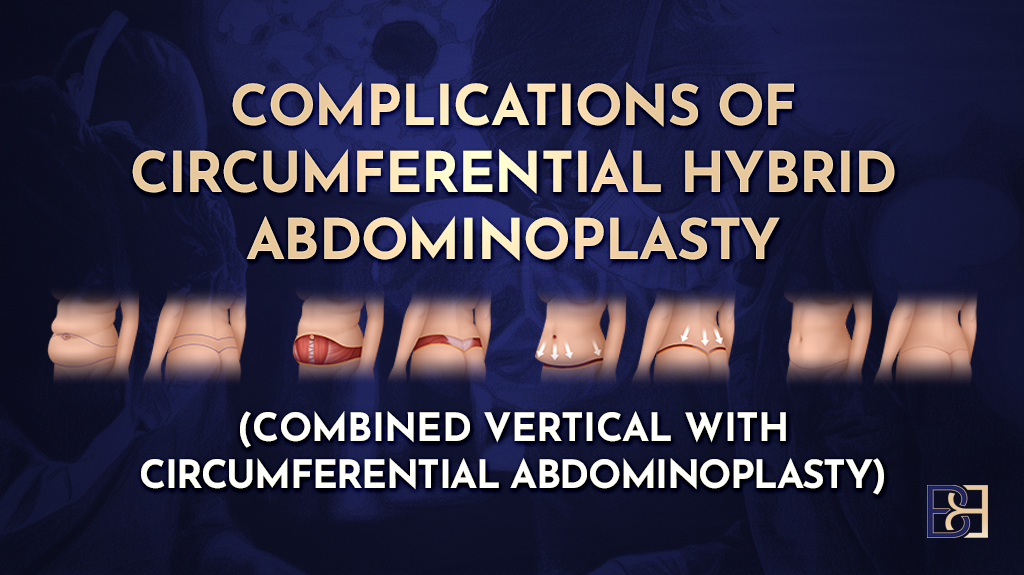
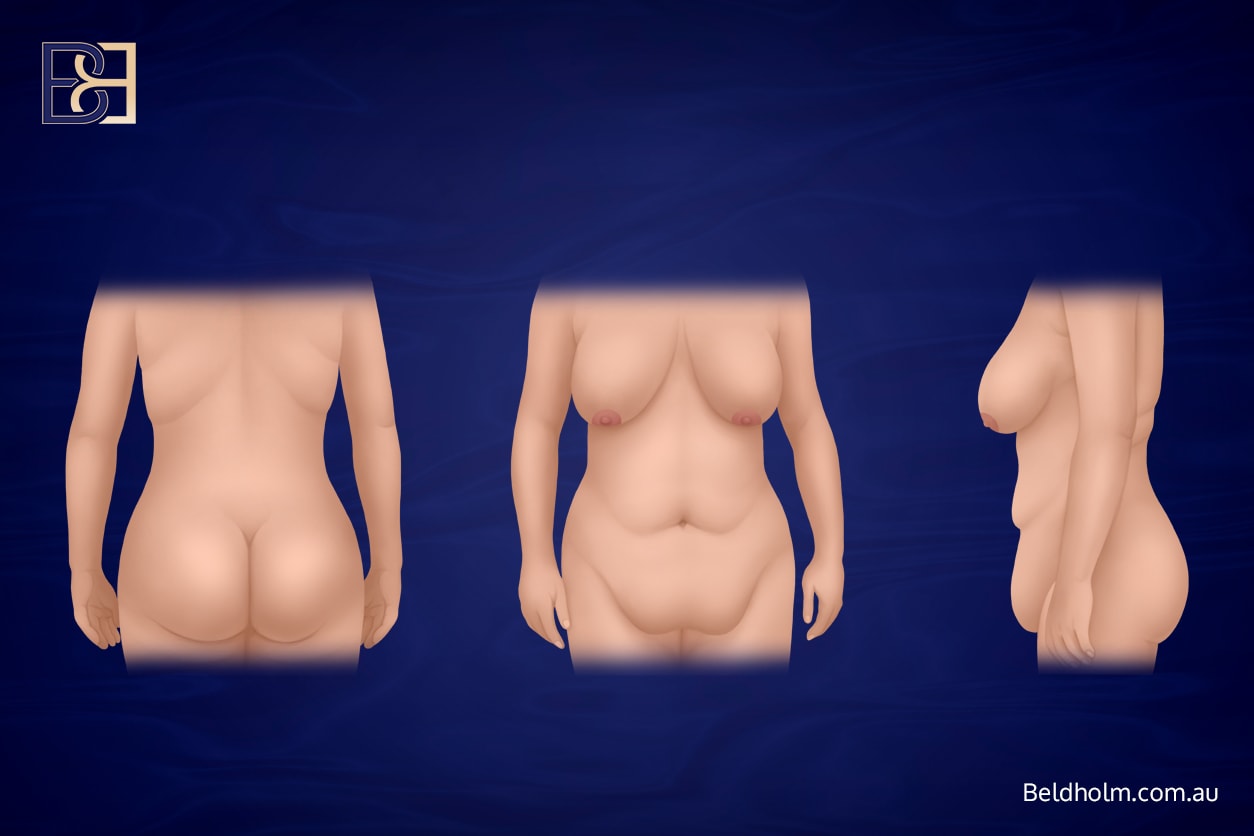
Circumferential hybrid abdominoplasty is an extensive body lift (belt lipectomy) procedure that combines a fleur de lis abdominoplasty with a circumferential abdominoplasty (belt lipectomy). This operation is most commonly considered by patients who have undergone significant weight loss, including after bariatric surgery or prolonged changes in body weight, and who are left with a large amount of excess skin and fat affecting the entire waistline.
This article provides an in‑depth, educational discussion of the complications of circumferential hybrid abdominoplasty. While many patients progress through surgery and recovery without major problems, this is a complex surgical procedure with a generally high level of physiological stress and a recognised complication rate that is higher than that of a standard tummy tuck (abdominoplasty) alone.
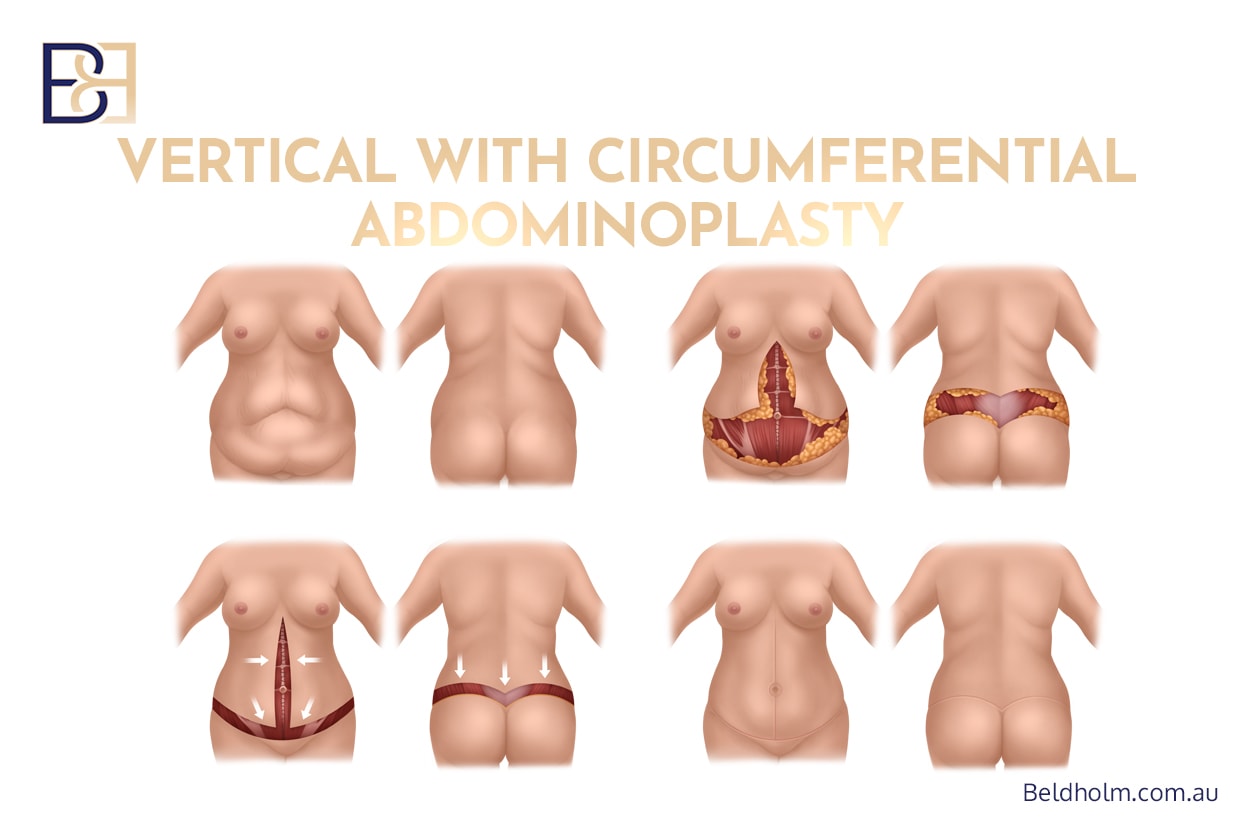
What Is a Circumferential Hybrid Abdominoplasty?
A circumferential hybrid abdominoplasty combines two established operations:
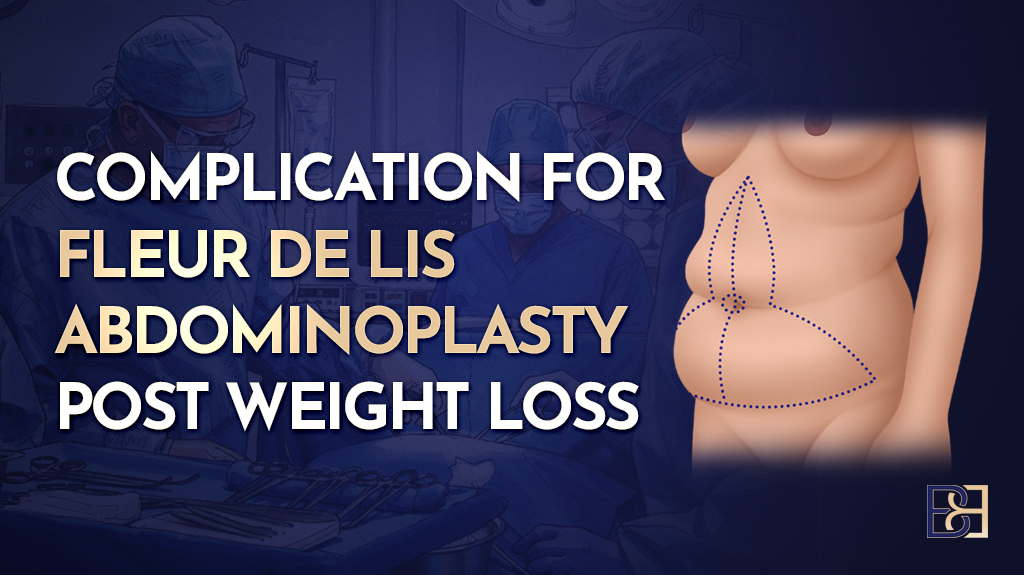
Fleur de lis abdominoplasty, which treats the vertical and horizontal excess skin of the anterior abdomen using a vertical midline incision combined with a lower horizontal incision.
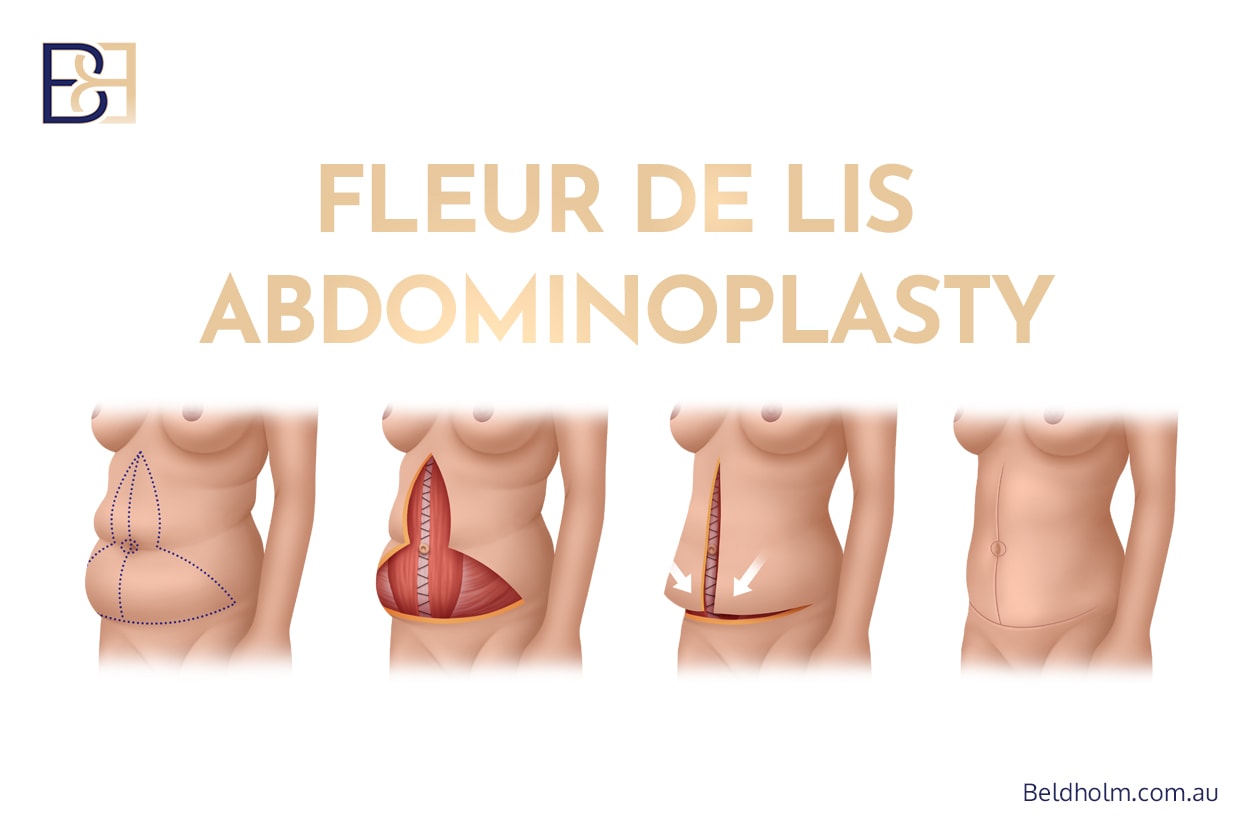
Circumferential abdominoplasty (belt lipectomy), which extends the incision around the entire waist to treat the lower back, flanks, and buttock region as part of a comprehensive lower body lift.
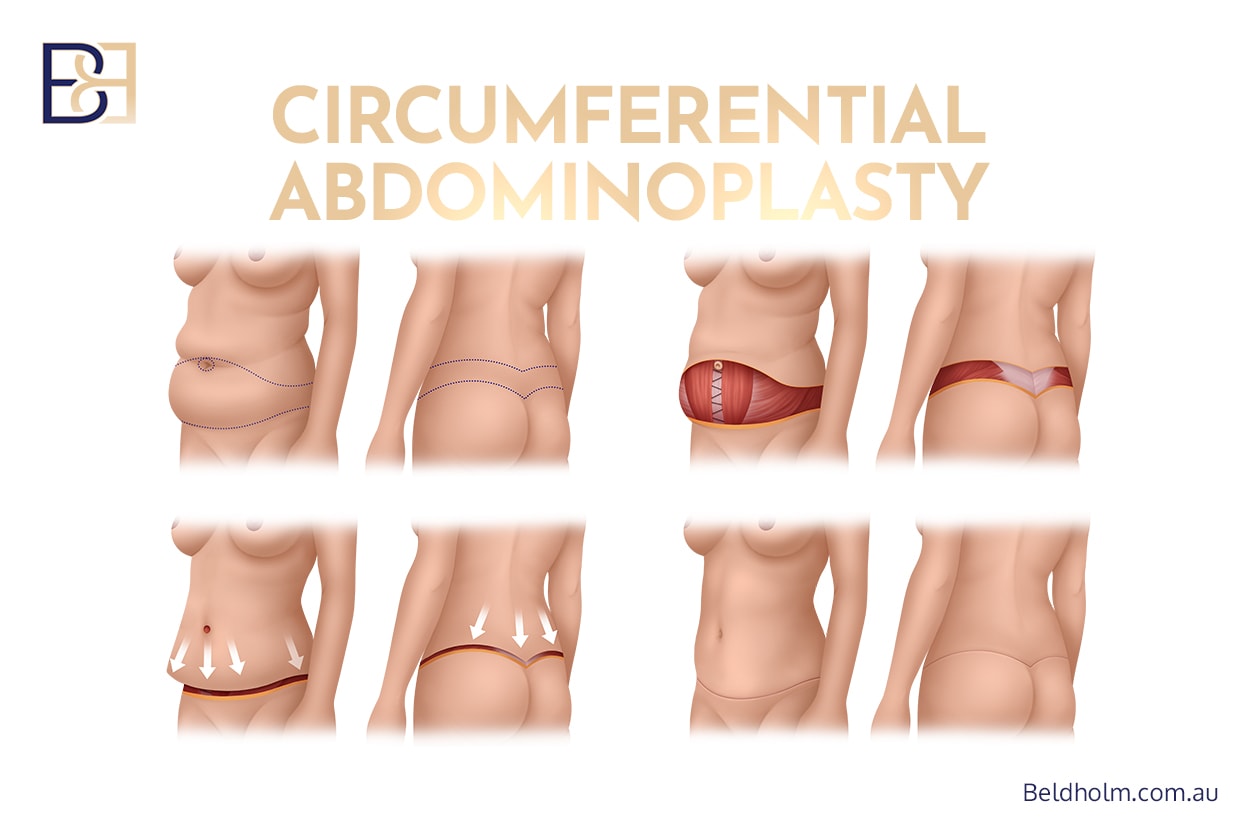
By combining these techniques, surgeons aim to remove extensive redundant skin, treat the abdominal wall contour, and focus on the circumferential skin laxity. This approach may be considered in patients who have undergone massive weight loss, experienced significant weight loss, or have marked significant skin laxity that cannot be adequately treated with a traditional abdominoplasty.
Why the Risk Profile Is Higher Than a Standard Tummy Tuck (abdominoplasty)
The complication rate associated with circumferential hybrid abdominoplasty is higher than that of a standard tummy tuck (Abdominoplasty) due to several factors:
- Long operative time
- Extensive undermining of the abdominal skin
- A long horizontal incision around the entire waist combined with a vertical incision
- Reduced blood supply to the skin flaps
- Larger volumes of excess tissue and excess skin and fat being removed
Patients who have achieved significant weight loss or massive weight loss may also have nutritional deficiencies or medical conditions that influence wound healing and recovery.
Common Complications
Wound Healing Problems
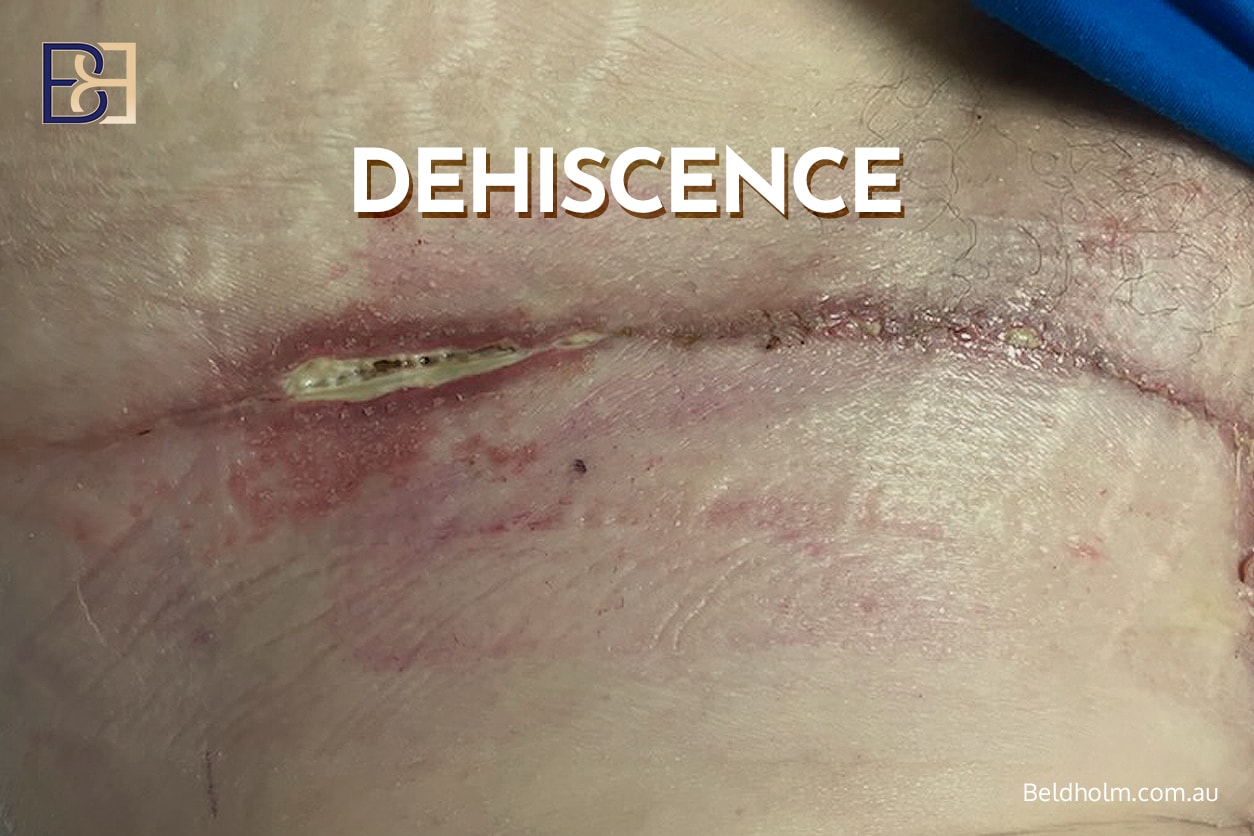
Wound healing problems are among the most frequently encountered issues following any body lift (belt lipectomy) procedure. These may include:
- Delayed wound healing
- Superficial wound separation
- Wound dehiscence at areas of increased tension
The junction between the vertical and horizontal incisions in a fleur de lis abdominoplasty is particularly vulnerable. Smoking, diabetes, nutritional deficiencies, and unstable weight loss patterns increase the risk of wound healing complications.
Seroma Formation
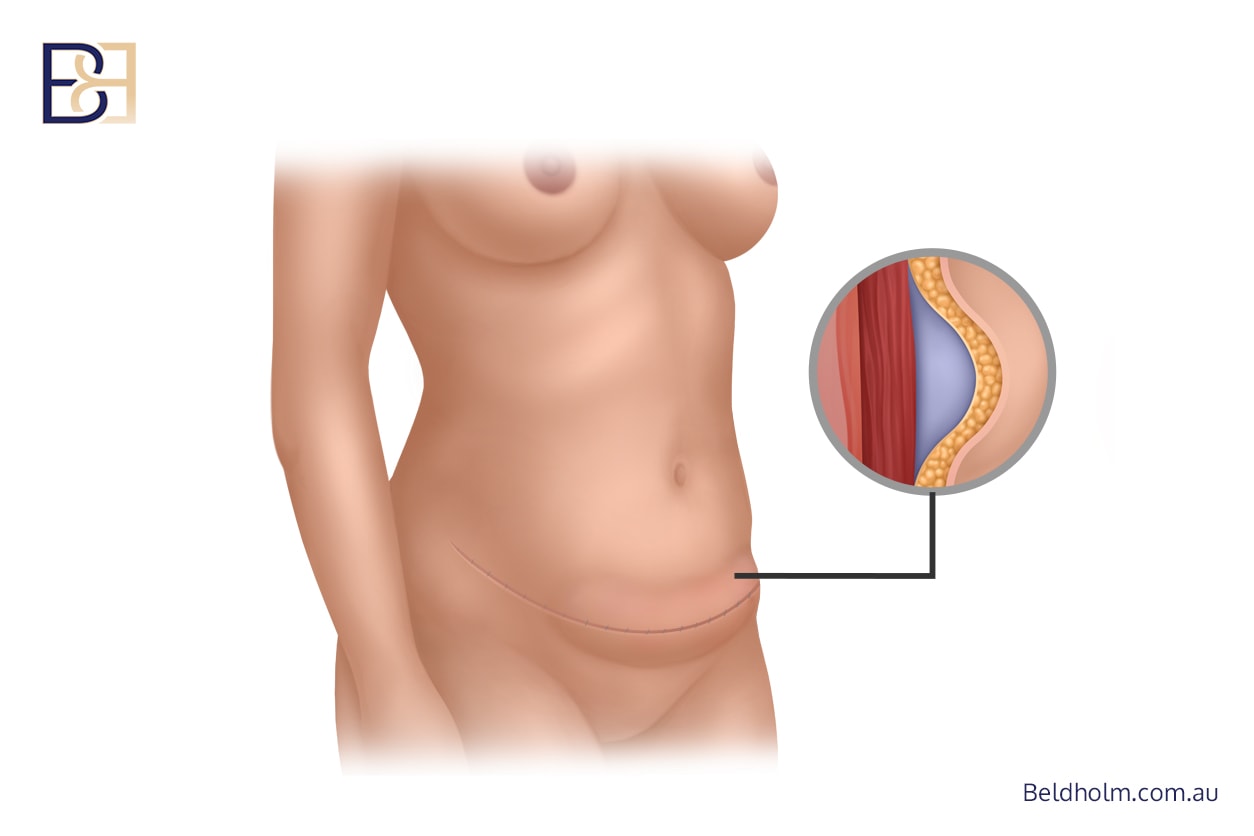
A seroma is a collection of fluid beneath the skin that may develop after extensive fat removal and soft‑tissue dissection. Seromas are relatively common following circumferential body contour procedures.
Patients may notice:
- Localised swelling
- A sense of fluid movement
- Asymmetry in the abdominal area
Management may involve needle aspiration, prolonged use of compression garments, or observation over time.
Infection
Wound infection is a recognised risk after major reconstructive body lift (belt lipectomy) procedures. Infection may present with increasing pain, redness, discharge, or fever.
Risk factors include:
- Long surgical duration
- Large wound surface area
- Diabetes or immune compromise
Prompt treatment is important to minimise progression to deeper infection or delayed healing.
Bleeding and Haematoma
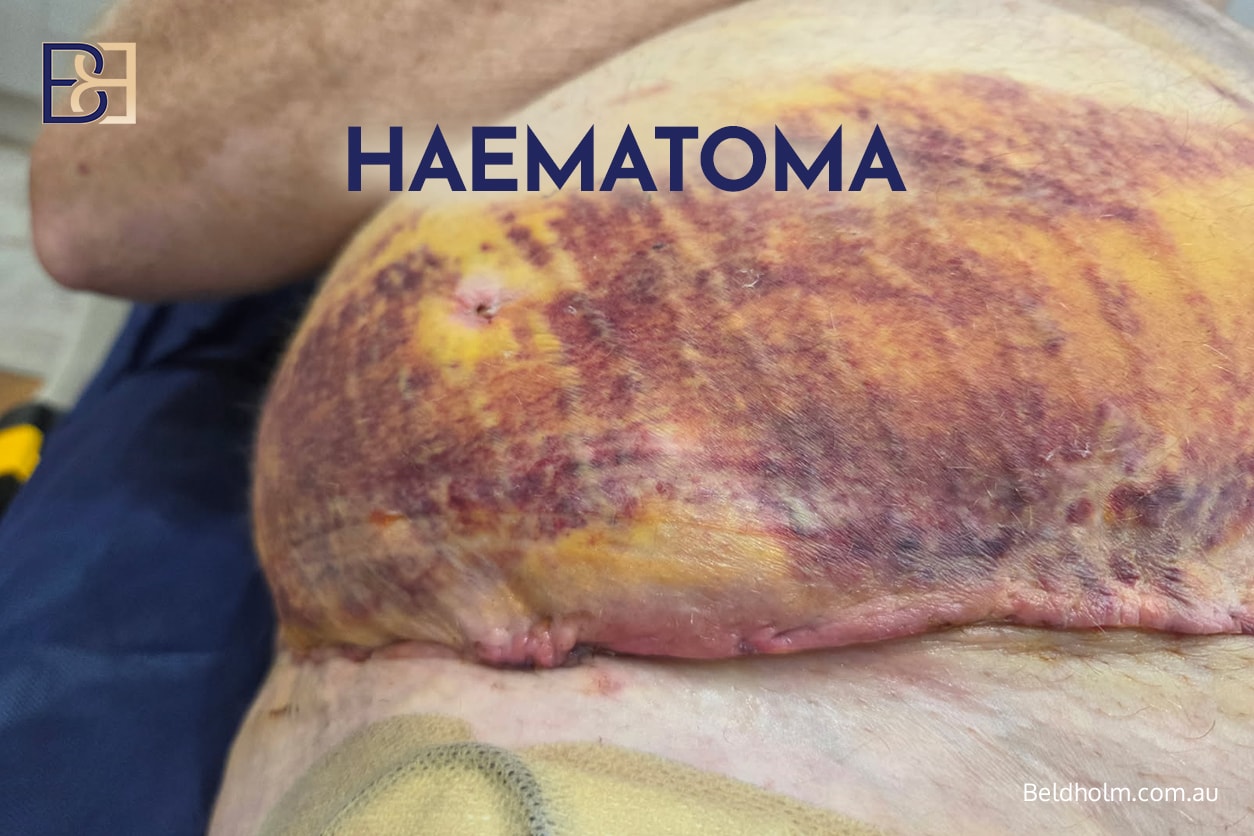
Bleeding under the skin can result in a haematoma, which may cause pain, swelling, and pressure on surrounding tissues. Some haematomas resolve without intervention, while others require surgical drainage.
Blood Clots
Blood clots, including deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, are serious but uncommon surgical risks following extensive lower body surgery.
Factors that increase risk include:
- Prolonged operative time
- Limited mobility during the early recovery period
- Higher BMI or a history of undergone massive weight loss
Preventative strategies are routinely used, but risk cannot be completely eliminated.
Sensory Changes and Nerve‑Related Complications
Altered sensation of the abdominal skin is common after abdominoplasty. The most commonly injured nerve in abdominoplasty is usually a branch of the intercostal nerves supplying the lower abdomen.
Patients may experience:
- Numbness
- Tingling
- Reduced sensitivity of the abdominal skin
In many cases, sensation resolves over time, but permanent sensory changes are possible.
Belly Button–Related Complications
The belly button (umbilicus) is repositioned during circumferential hybrid abdominoplasty. Possible complications include:
- Delayed healing
- Partial skin loss
- Infection
- Scarring or asymmetry
These risks are higher when blood supply to the abdominal skin is reduced by extensive dissection.
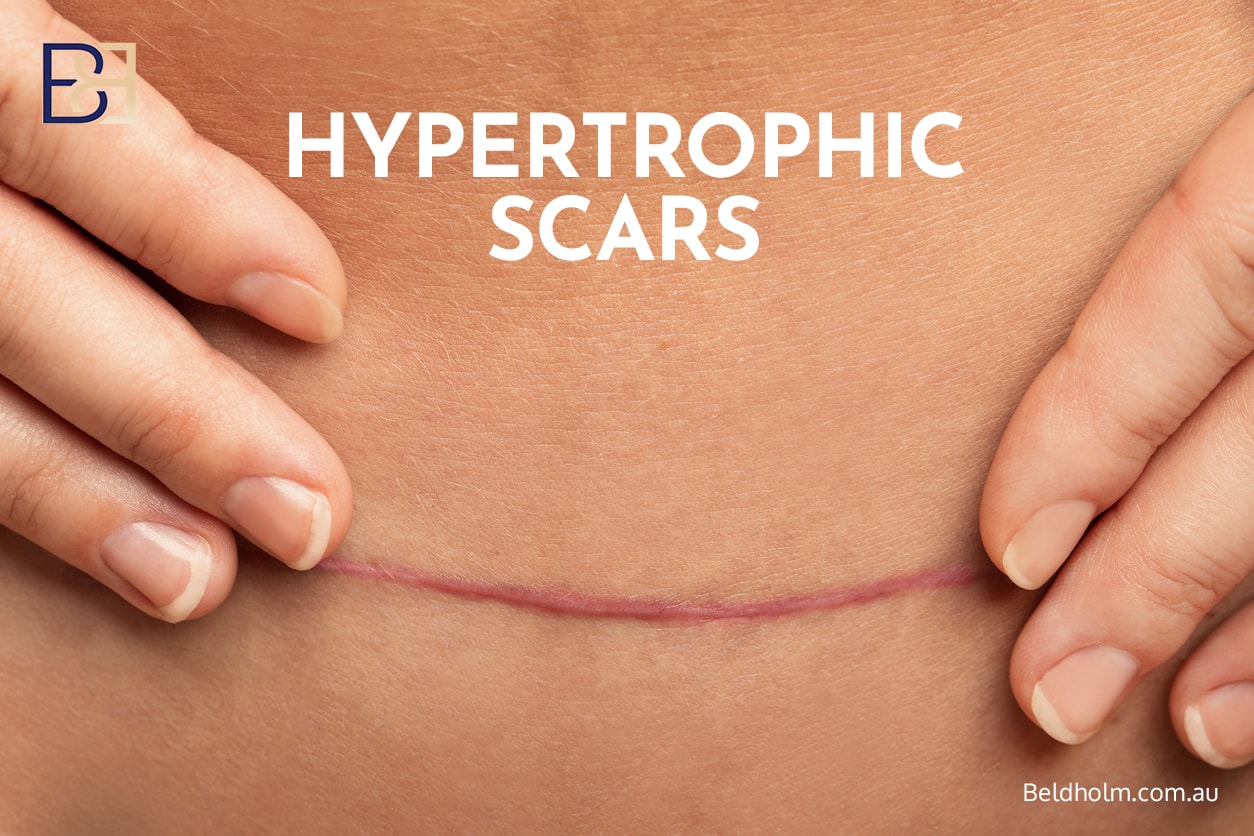
Scarring After Circumferential Hybrid Abdominoplasty
Scarring is an inevitable outcome of this surgical procedure. Patients should expect:
- A long circumferential scar around the entire waistline
- A vertical midline scar associated with the fleur de lis abdominoplasty
Some patients may develop thickened, widened, or uneven scars. Scar maturation often takes 12 to 18 months and varies between individuals.
Abdominal Wall and Muscle‑Related Complications
Repair of the abdominal muscles may be performed to treat muscle separation (Diastasis recti) or abdominal wall weakness. Potential complications include:
- Muscle repair failure
- Persistent abdominal wall discomfort
- Functional limitations during recovery
These issues may affect physical activity during the healing process.
Impact of Weight Changes After Surgery
Significant weight loss or weight gain after surgery can influence outcomes and complication risks. Patients are generally advised to reach and maintain a stable goal weight before surgery.
Ongoing weight changes may contribute to:
- Recurrent loose skin
- Increased tension on scars
- Altered body contour results
Less Common but Serious Complications
Less common complications may include:
- Skin necrosis
- Major wound infection requiring hospital treatment
- Systemic complications related to anaesthesia
For this reason, circumferential hybrid abdominoplasty is not everyone, even among patients with extensive excess skin after significant weight loss.
Pre‑operative Risk Assessment

A detailed initial consultation and comprehensive evaluation are essential. Assessment typically includes:
- Review of medical history
- Assessment of weight stability and nutrition
- Examination of abdominal skin, fat, and muscle
- Discussion of alternative or staged procedures
In some cases, a staged approach such as a lower body lift (belt lipectomy) followed by additional procedures (for example thigh lift (Thighplasty) surgery, breast reduction (Reduction mammoplasty), or surgery to the upper arms (Brachioplasty)) may reduce overall risk.
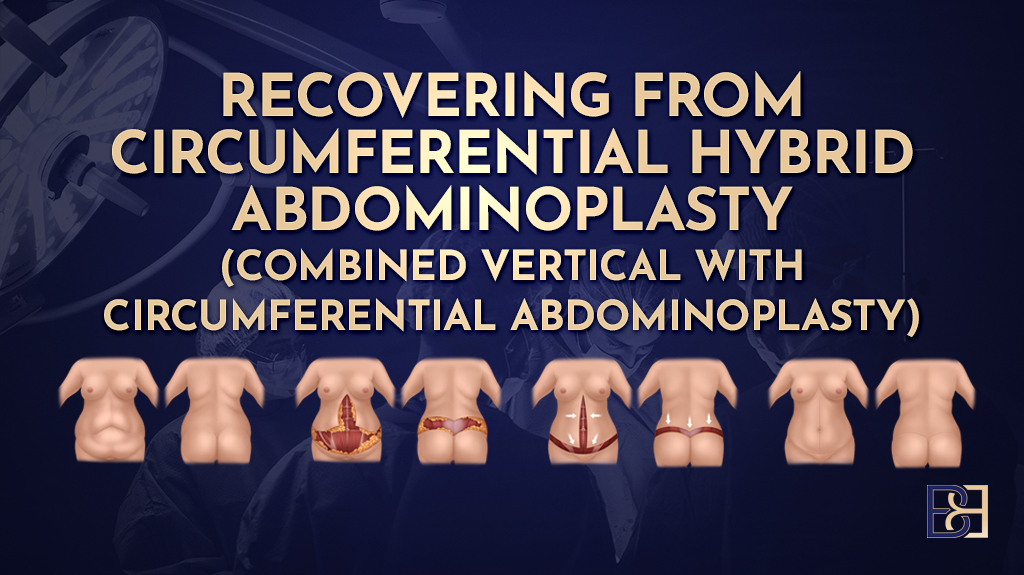
Recovery and Monitoring

The recovery time for a circumferential tummy tuck (abdominoplasty) is longer than for a standard abdominoplasty. Most patients require:
- Several weeks away from work
- Restricted physical activity
- Ongoing use of compression garments
- Close postoperative monitoring during the first few weeks
Early identification of complications supports timely treatment and optimal healing.
Frequently Asked Questions

Book your appointment online now
What is the most common complication of abdominoplasty?
Wound healing issues, including delayed healing and minor wound breakdown, are the most common complications.
What is a hybrid tummy tuck (abdominoplasty)?
A hybrid tummy tuck (abdominoplasty) combines techniques such as fleur de lis abdominoplasty and circumferential abdominoplasty to treat both vertical and horizontal excess skin.
What is the recovery time for a circumferential tummy tuck (abdominoplasty)?
Recovery usually extends over several months, with the most intensive phase in the first 6 to 8 weeks.
Final Considerations
Circumferential hybrid abdominoplasty can remove large amounts of excess skin and fat and treat functional problems associated with redundant tissue. However, it is a major body lift (belt lipectomy) procedure with recognised risks and a higher complication rate than less extensive operations.
Careful patient selection, realistic expectations, and a thorough understanding of potential complications are essential. A consultation with a qualified Specialist Surgeon is required to determine whether this operation is appropriate for an individual patient.