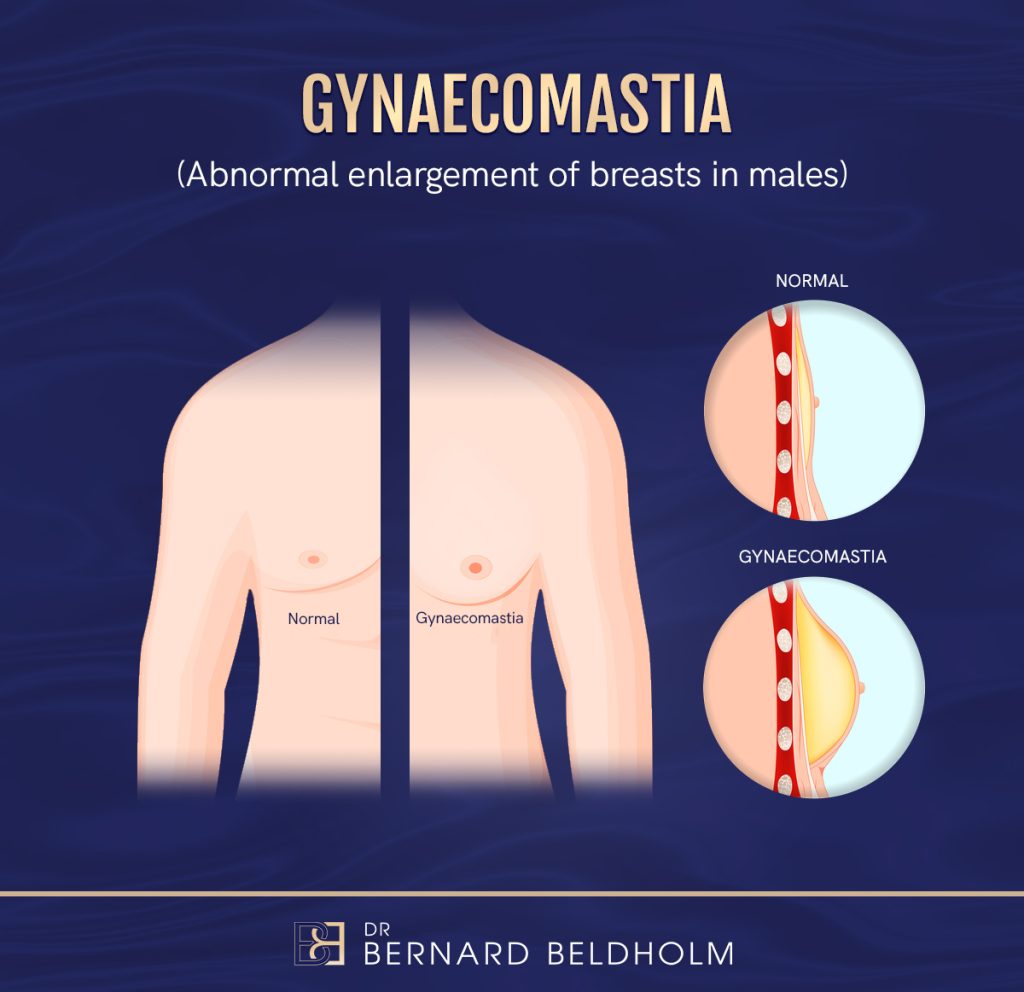
Gynaecomastia, characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males, commonly arises from hormonal imbalances, medications, or certain health conditions. Treatment options vary, from lifestyle adjustments and hormonal therapies for milder cases to surgical intervention for more severe conditions.
Understanding Gynaecomastia
Book your appointment online now
Gynaecomastia is characterised by the enlargement of breast tissue in males, affecting either one or both breasts. Distinguishing between true gynaecomastia, involving glandular breast tissue growth, and pseudo gynaecomastia, related to excess chest fat, is important. This distinction helps in deciding the suitable treatment approach. True gynaecomastia often presents as a firm, rubbery swelling beneath the nipple, a feature that can persist even in individuals with low body fat, leading to enlarged breasts.
Disclaimer: Operation performed by Dr Bernard Beldholm. Adult content, surgery has risks; individual results vary, seek 2nd opinion. Please see the full disclaimer.
The condition is not as rare as one might think. In fact, it’s estimated that up to 70 percent of males develop gynaecomastia at some point in their lives, particularly during puberty. While gynaecomastia is primarily an aesthetic issue and not typically harmful to health, it can have significant psychological impact.
Causes of Gynaecomastia
Knowing the causes of gynaecomastia aids in both prevention and treatment. Gynaecomastia typically arises from an imbalance between testosterone and oestrogen levels. This imbalance can occur due to various factors, including hormonal changes during puberty or aging and the use of certain medications, including idiopathic gynaecomastia.

Aside from hormonal imbalances, other significant causes include specific medications and underlying medical conditions. For example, anabolic steroids and certain heart medications have been linked to the development of gynaecomastia. Additionally, medical conditions such as chronic liver disease and thyroid disorders can disrupt hormone levels, leading to the growth of breast tissue in men.
Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalances are a primary cause of gynaecomastia. Specifically, a drop in testosterone levels and an increase in oestrogen levels can increase breast tissue development in males. This imbalance of hormone changes can be particularly pronounced during puberty and later in life, as natural hormone levels fluctuate.
Various health issues such as liver failure, thyroid disorders, and obesity can lead to these hormonal imbalances. Conditions like hypogonadism, where the body doesn’t produce enough testosterone, and hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid gland is overactive, are known contributors.
Managing these underlying health issues is essential in preventing gynaecomastia.
Medication and Drug Use
Certain medications and drugs are well-known culprits in the breast development and of gynaecomastia. Anabolic steroids, often misused for muscle building, can significantly disrupt hormonal balance, leading to increased breast tissue in males. Similarly, calcium channel blockers, used to treat hypertension, have been associated with gynaecomastia.
Limiting alcohol intake can help, as it can increase estrogen levels, worsening the problem of estrogen excess.
Medical Conditions
Medical conditions play a significant role in the development of gynaecomastia. Chronic liver disease, for example, can alter hormone levels, leading to an increase in breast tissue in men. Controlling these underlying conditions helps prevent hormonal fluctuations that lead to gynaecomastia.
Additionally, certain medications, including anti-androgens and anabolic steroids, disrupt hormonal balance and can result in gynaecomastia due to their oestrogen-like effects. Tackling these medical issues and medications is key to effectively managing the condition.
Symptoms of Gynaecomastia
The symptoms of gynaecomastia can vary but primarily affect the breast area. Common signs include:
- swelling or soreness in the breast area or nipples
- changes in the skin over the breast or nipple, such as dimpling or rashes
- discharge or bleeding from the nipple, which warrants immediate medical attention
Gynaecomastia can be temporary, particularly during puberty when hormone levels fluctuate. This form cause gynaecomastia, known as pubertal gynaecomastia, typically resolves on its own. However, if the condition persists, it may require medical intervention to treat the underlying causes and symptoms.
Diagnosing Gynaecomastia

Diagnosing gynaecomastia starts with a detailed medical history and physical examination. Doctors look for specific signs such as the enlargement of breast tissue in males, which can affect one or both breasts. Persistent pain in the breast or nipple region is a sign that should prompt a consultation with a healthcare provider.
Additional diagnostic steps involve blood tests and imaging studies. Blood tests measure hormone levels and identify any imbalances. Imaging studies, such as mammograms and ultrasounds, are employed to evaluate the extent of breast tissue growth and to differentiate between benign and malignant conditions.
Physical Examination
During a physical exam, physicians differentiate true gynaecomastia from pseudo-gynaecomastia by assessing the consistency and location of breast tissue. They palpate the breast tissue, abdomen, and testicles to check for abnormalities and assess for glandular proliferation around the nipple area, which indicates true gynaecomastia.
Blood Tests
Blood tests for diagnosing gynaecomastia typically include hormonal evaluations to identify imbalances in oestrogen and testosterone levels. These tests can uncover conditions like hypogonadism or hyperthyroidism that cause hormone shifts.
Liver function tests and other assessments are also conducted to rule out additional medical conditions.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies like mammograms and ultrasounds are vital for assessing gynaecomastia. Mammograms are particularly useful in distinguishing between benign and malignant lesions, providing a clear picture of the various male breast cancer and tissue changes.
These imaging techniques assess the severity and nature of the condition.
Treatment Options for Gynaecomastia
Treating gynaecomastia involves a range of options, from lifestyle adjustments to medical interventions. Non-surgical treatments include hormone therapies and off-label medications designed to treat the underlying hormonal imbalances. These treatments can be effective, particularly in mild cases or when the condition is detected early. To treat gynaecomastia, it is essential to consider these various approaches.
For more severe or persistent cases, surgical options may be necessary. Gynaecomastia surgery, also known as male breast reduction, is often the preferred treatment. This procedure aims to remove excess glandular tissue and fat, providing a flatter, more contoured chest profile. The choice of treatment depends on the individual’s specific circumstances and the severity of the condition.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments treat hormonal imbalances and mitigate symptoms. Hormone therapies, such as testosterone replacement, can help increase testosterone levels and reduce breast tissue growth. Doctors may prescribe off-label medications like tamoxifen or raloxifene in some cases.
A balanced diet and exercise can also help manage gynaecomastia. Reducing alcohol consumption and avoiding certain medications can help prevent and treat gynaecomastia.
Surgical Treatments
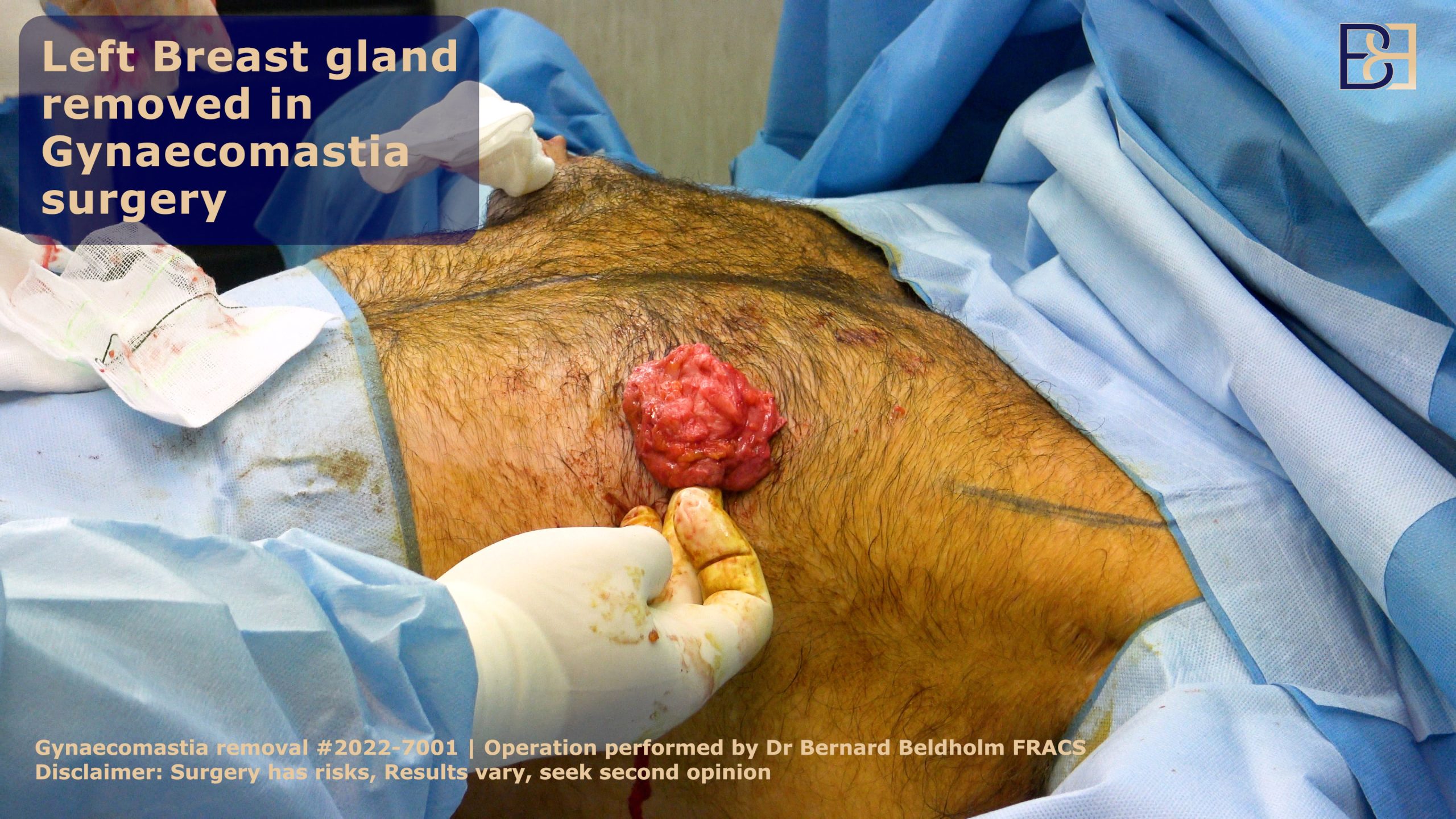
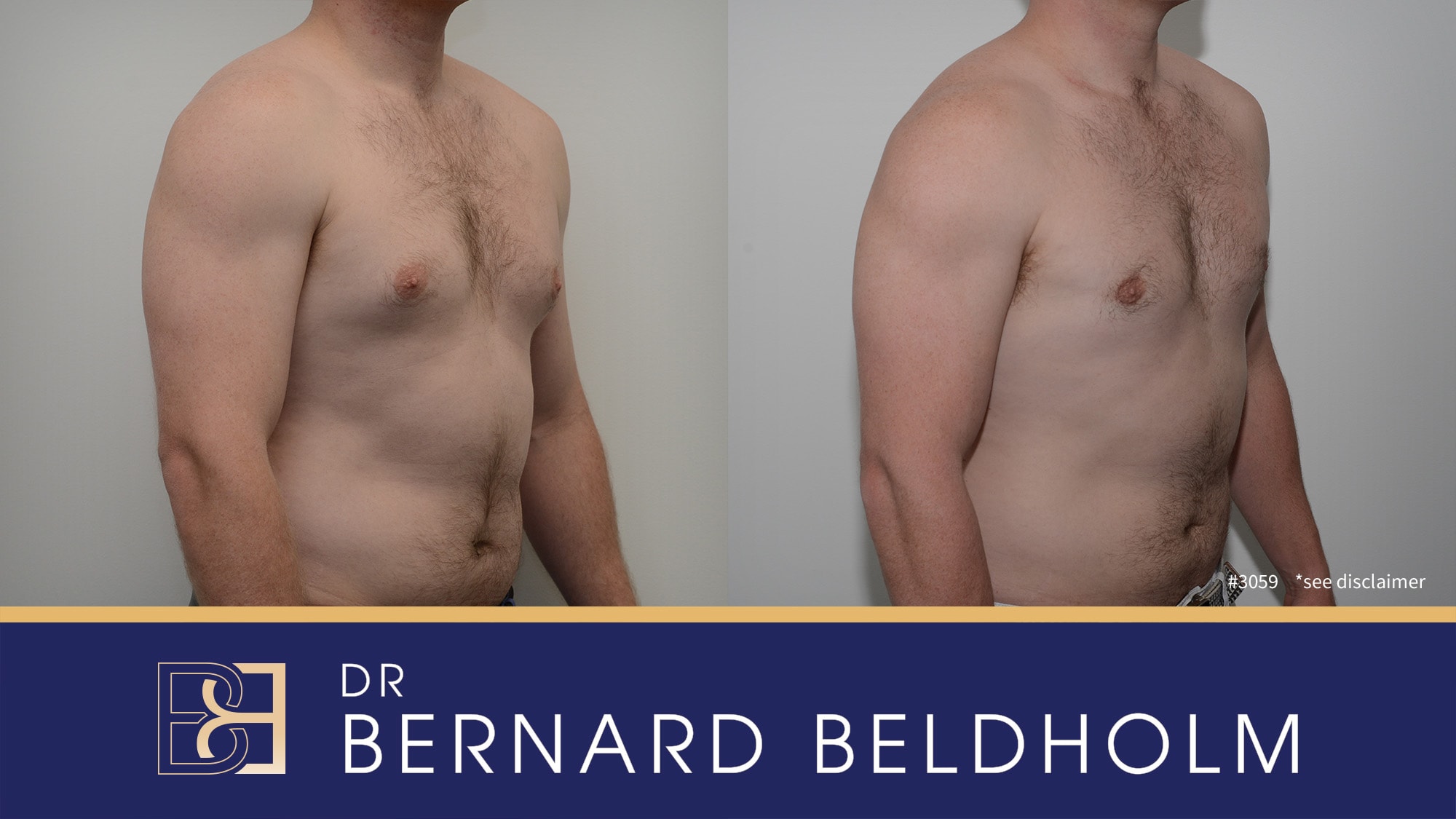
Gynaecomastia surgery, also known as male breast reduction, involves removing excess glandular tissue and fat to achieve a flatter chest profile. This surgery often uses techniques like liposuction (Suction-assisted lipectomy). Dr. Bernard Beldholm, a specialist surgeon, performs this surgery typically in a private hospital in Maitland.
Surgery is often the preferred treatment for gynaecomastia because it provides immediate and noticeable results. However, surgery carries risks and requires a recovery period, which will be discussed next.
Recovery After Gynaecomastia Surgery
Recovery from gynaecomastia surgery involves several stages, each crucial for achieving the best results. Most patients can resume normal activities within two days, but complete recovery typically spans 4 to 6 weeks, depending on the individual’s healing rate. Following post-surgery recommendations ensures proper healing and reduce complications.
Full healing can take up to 18 months, requiring ongoing attention to recovery practices. Changes in nipple or breast sensation can occur, which might be temporary or permanent. Knowing what to expect during recovery helps patients manage their post-surgery journey effectively.
Immediate Post-Surgery Care
Immediately after gynaecomastia surgery, patients may experience common side effects such as nausea and grogginess due to anesthesia. Bruising or soreness from the IV drip is also common.
Wearing compression garments for at least four weeks post-surgery minimises swelling and supports healing.
Long-Term Recovery
Long-term recovery involves several steps to ensure the best outcomes. Patients should avoid strenuous activities for the first two weeks and may experience mild pain, numbness, and tenderness in the chest area during this period. Massage techniques on the treated area should begin three weeks after surgery to aid in healing and reduce scar tissue.
Most swelling typically subsides by the six-week mark, at which point normal activities can generally resume. Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding steroids, and monitoring underlying conditions are key lifestyle changes for sustaining surgery results.
There is a small chance gynaecomastia may return after surgery, with research indicating around a 10% chance.
Risks and Complications of Gynaecomastia Surgery
As with any surgical procedure, gynaecomastia surgery carries certain risks and potential complications. Patients may experience adverse reactions to anaesthesia, which can include allergic reactions or even cardiovascular complications. Additionally, there is a risk of bleeding, which can lead to the formation of a haematoma, as well as the possibility of infection.
Other potential complications include persistent breast pain, fluid accumulation (seroma), and unfavourable scarring. Some patients might notice asymmetry in breast appearance or experience damage to deeper structures, such as nerves and blood vessels, which can be temporary or permanent.
Discussing these risks with your surgeon is essential for making an informed decision about the procedure.
Preventing Gynaecomastia

Preventing gynaecomastia often involves lifestyle modifications to maintain a healthy hormonal balance. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Change your diet to include more whole foods and reduce processed foods.
- Increase physical activity to help reduce body fat, which is crucial since higher body fat can contribute to the development of gynaecomastia.
- Limit alcohol consumption, as it can exacerbate breast enlargement by increasing oestrogen levels.
By implementing these changes, you can work towards preventing gynaecomastia effectively.
Avoiding the use of anabolic steroids and certain medications known to affect hormone levels can prevent drug-induced gynaecomastia. Regular medical check-ups to manage conditions like thyroid disorders and chronic liver disease are essential to prevent hormonal imbalances causing gynaecomastia.
Living with Gynaecomastia
Living with gynaecomastia can be challenging due to the psychological impact it has on men. Many experience feelings of anxiety, embarrassment, and depression related to their condition. The psychological effects can lead to a sense of emasculation and fears about diminished masculinity. It’s important for men to seek emotional support from family and friends to cope with these feelings.
One study concluded: “Gynecomastia has a significant negative impact on primarily the psychosocial well-being of affected adolescent patients. … Psychosocial impact was not affected by graded severity of disease.” (1)
Adolescents with gynaecomastia are particularly vulnerable, often facing severe issues with identity, which can lead to significant psychological distress. Psychological support and counselling are crucial for these individuals, helping them navigate the emotional challenges associated with gynaecomastia.
Thus, treating the psychological impact is as important as treating the physical symptoms.
Summary
Gynaecomastia is a common yet often misunderstood condition that affects many men at various stages of life. It is primarily caused by hormonal imbalances, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions. Understanding the symptoms and seeking proper diagnosis through physical exams, blood tests, and imaging studies is crucial for effective treatment. Both non-surgical and surgical treatments are available, with gynaecomastia surgery being the preferred option for many.
Preventing gynaecomastia involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding certain medications, and managing underlying health conditions. For those living with the condition, treating the psychological impact is essential. With the right support and treatment, men can manage gynaecomastia effectively. Remember, seeking professional help and making informed decisions are key steps in this journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is gynaecomastia?
Gynaecomastia is when guys experience swelling of their breast tissue. It’s pretty common and can happen for various reasons.
Can gynaecomastia return after surgery?
Yes, gynaecomastia can come back after surgery, but the chances are low, about 10%. So, while surgery is usually effective, it’s good to be aware of the possibility.
What condition is often responsible for excess breast tissue in men?
Gynaecomastia is the usual culprit for excess breast tissue in men. It’s a common condition that can happen due to hormonal changes or various other factors.
What is another name for gynaecomastia surgery?
Gynaecomastia surgery is also known as male breast reduction. It’s a go-to option for guys looking to flatten their chest.
Book your appointment online now
References
Nuzzi LC et al. “Psychosocial impact of adolescent gynecomastia: a prospective case-control study.”, Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery. 131(4):890-896, 2013 Apr.






